Biometric Modalities: The Hardware Perspective

The high level of security offered by biometric technology has led to them becoming commonplace within many sensitive industries such as law enforcement and border security. Biometrics extends far beyond just fingerprint scanners; there are multiple different modalities available for biometric analysis, all offering different use cases and strengths.
The different biometric modalities require different hardware to capture the biometric data. This guide sets out a few things to consider when choosing biometric hardware.
Different types of biometric modalities
- Fingerprint
- Face
- Iris
- Voice
- Palm
- Hand Geometry
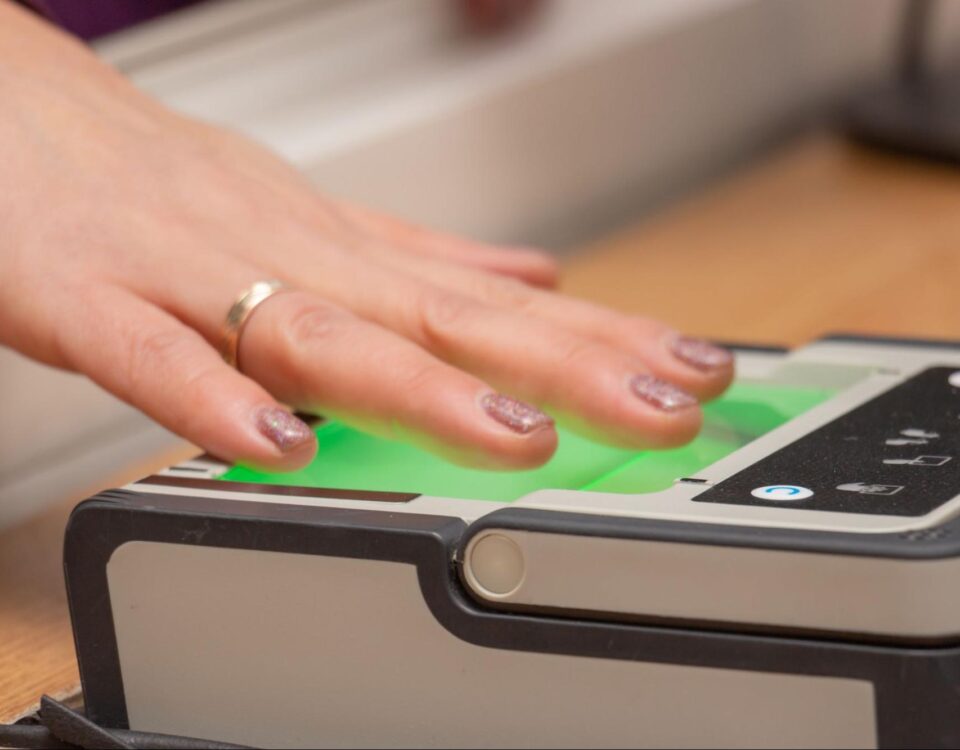
Fingerprint Scanners
Fingerprints are unique to the individual. Scanning of the fingerprint offers a secure biometric solution that is popular for access control and identification purposes among many other use cases. Whilst fingerprint scanners are one of the oldest biometric identifiers, they are still prevalent and popular today due to the advanced level of security offered.
There is a wide selection of fingerprint readers on the market, varying not just in brand and budget but also in applications, technology and support.
Things to consider when choosing a fingerprint reader
- Optical, Capacitive, Ultrasonic, Thermal or Hybrid
- Connection
- Supported OS
- Resolution
- Image Capture Area; Physical and Effective
- Fingerprint Image Size
- Sensor Type
- Device Size
- Device Weight
- Operating Temperature
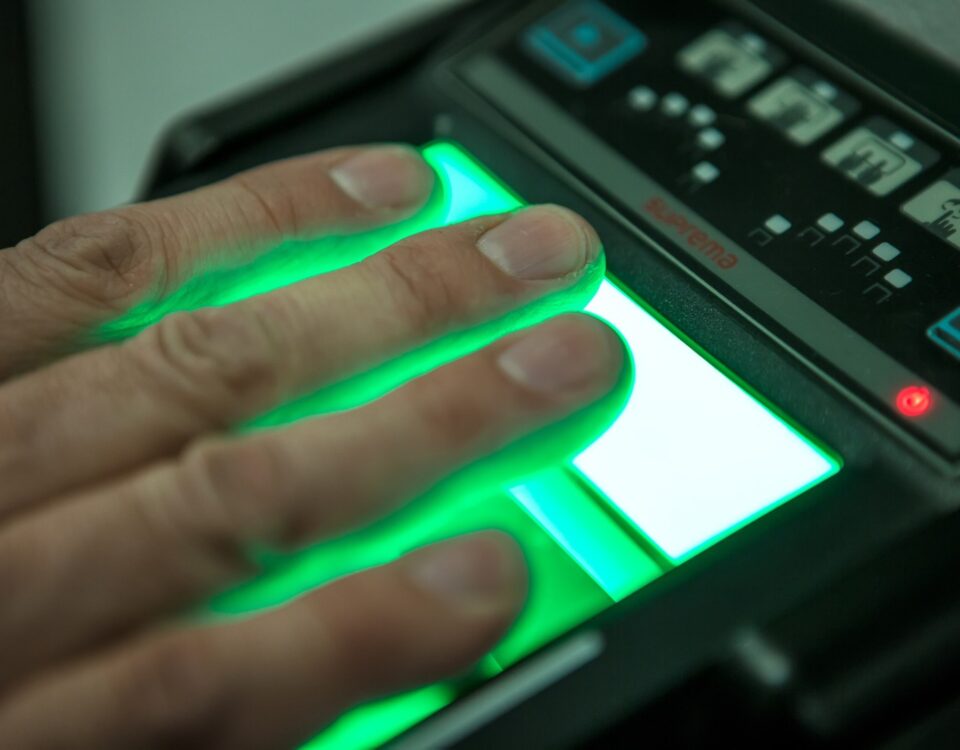
Understanding the differences between optical, capacitive, ultrasonic, thermal and hybrid biometric fingerprint devices
Whilst they all perform largely the same purpose, the technological process used varies between scanners. The oldest fingerprint identification method is optical scanning, where a fingerprint is captured as an image, and then algorithms are used to extract the fingerprint data and characteristics.
Capacitive scanners are a popular choice within the smartphone market. These types of scanners use an array of capacitor circuits to collect data, connected to conductive plates to track the characteristics of the fingerprint.
The latest innovation within this particular biometric modality field is the development of ultrasonic scanners, which have already started to feature within some innovative smartphones. An ultrasonic pulse is sent to the finger, and the reflections are analyzed to identify the ridges and pores of the fingerprint.
Thermal scanners are a rarer form of fingerprint device hardware; they function by sensing the temperature difference between the contact surface and the fingerprint.
Variations in Capture Devices
Depending on the use case, there is variation in how the fingerprint is captured, and how many fingerprints are scanned at any one time. Often, choosing between which type of capture device is needed will depend on whether your requirements prioritize accuracy, portability or a combination of the two. The standard options to choose from include:
Choosing the right fingerprint device for your project can be difficult, regardless of your knowledge and expertise in biometric hardware.
The Biometric Supply team is on-hand to offer vendor-independent advice to help you choose the right device for your project.
Iris Scanners
Everyone’s irises have a unique pattern and color shade. As irises can’t be altered or modified, iris authentication is an ideal solution in personal identification situations where a high-level of security is required. For example, iris authentication is becoming commonplace within the healthcare and immigration sectors.
How do they work?
Scanners for biometric iris authentication work by sending an invisible infrared light to capture an image of the eye. The iris is then detected and extracted from the rest of the image.
An iris scanner typically collects around 240 biometric features from a scan of the iris. To ensure this data is clean, other parts of the image such as the eyelid are removed from the image to be analyzed. Other common parts that are excluded include eyelashes and reflections that could block part of the iris.
Once these have been removed, it leaves a set of pixels that only includes the iris, ready to be analyzed. The bit pattern that encodes the information of the iris will be extracted. This bit pattern will be digitized, so that it can then be used for either iris verification or iris identification. Iris verification is the one-to-one matching of the template, whereas iris identification will compare one-to-many.
Differences between Iris Scanning devices
The primary difference between iris scanners is whether they are single iris capture or dual iris capture scanners. Within these two distinct types of iris scanners exist a range of hardware solutions that are suitable for indoor or outdoor use, as well as suitable for a broad range of expertise within biometric device usage.
A main differential is the distance at which the iris capture takes place, a distance that can vary greatly between different devices. The more advanced scanners even offer multi-positional iris illumination, providing the opportunity to authenticate an iris even if the subject is wearing eyewear.
It is important to check whether your usage of an iris scanner requires a specific certification such as an ISO standard. If you are unsure, the Biometric Supply team can offer vendor-independent advice to ensure that you find the right device for your requirements.
Multimodal Biometrics
There are products available that offer multimodal biometric authentication, offering greater flexibility and capability for your biometric requirements. One example is the VistaEY2P, also known as the VistaEY2-02, which offers dual iris capturing capabilities as well as face capture with LiveEye anti-spoof detection.
Having a multimodal biometric identification system is popular for organizations that do not require or desire the higher level of specialism offered by the single modality scanners.
Other products, such as the CredenceTWO, combine biometric fingerprint sensors with smart card reading, offering versatility with regard to enrollment capabilities.
Choosing the right biometric hardware for your requirements
Given the range of solutions and products on the market, choosing the right biometric hardware for your requirements can be difficult.
This is why our team is on-hand to provide the best vendor-independent advice to ensure you can select the most suitable biometric hardware for your project.
On all of our product pages, you can easily ask a question relating to the product, or you can contact our team who will happily assist you.